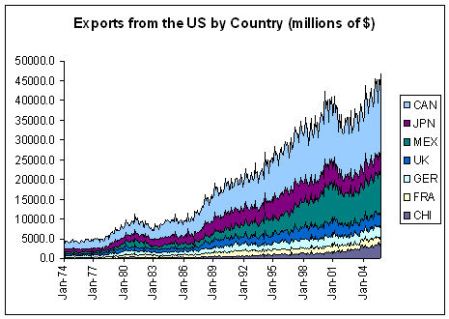
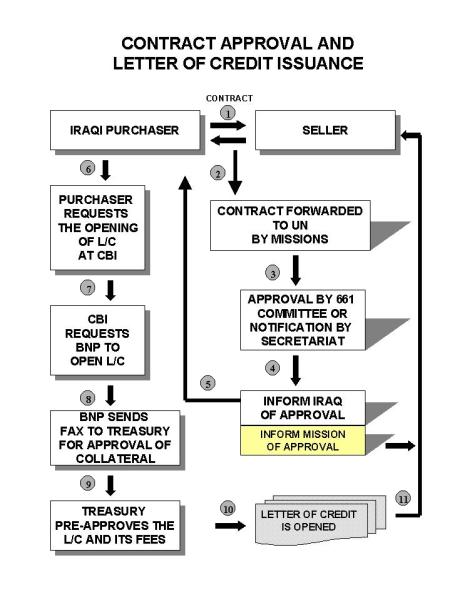
Common Stock
The term common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. It is called “common” to distinguish it from preferred stock. In the event of bankruptcy, common stock investors receive their funds after preferred stock holders, bondholders, creditors, etc.
when people talk about stocks they are usually referring to this type which is known as Common stock is, well, common. . In fact, the majority of stock is issued is in this form. We basically went over features of common stock in the last section. Common shares represent ownership in a company and a claim (dividends) on a portion of profits. Investors get one vote per share to elect the board members, who oversee the major decisions made by management.
Over the long term, common stock, by means of capital growth, yields higher returns than almost every other investment.
Common stock is usually voting shares, though not always. Holders of common stock are able to influence the corporation through votes on establishing corporate objectives and policy, stock splits, and electing the company’s board of directors.
The term common stock is a form of corporate equity ownership, a type of security. It is called “common” to distinguish it from preferred stock. In the event of bankruptcy, common stock investors receive their funds after preferred stock holders, bondholders, creditors, etc.

when people talk about stocks they are usually referring to this type which is known as Common stock is, well, common. In fact, the majority of stock is issued is in this form. We basically went over features of common stock in the last section. Common shares represent ownership in a company and a claim (dividends) on a portion of profits. Investors get one vote per share to elect the board members, who oversee the major decisions made by management.
Over the long term, common stock, by means of capital growth, yields higher returns than almost every other investment.
Common stock is usually voting shares, though not always. Holders of common stock are able to influence the corporation through votes on establishing corporate objectives and policy, stock splits, and electing the company’s board of directors.




 Posted by riya13
Posted by riya13